Exporting for Android
Exporting for Android has fewer requirements than compiling Godot for it. The following steps detail what is needed to setup the SDK and the engine.
Download the Android SDK
Download and install the Android SDK from http://developer.android.com/sdk/index.html
Install OpenJDK or Oracle JDK
Download and install OpenJDK or Oracle JDK. Version 6 and 8 are known to work, some users have reported issues with the jarsigner (used to sign the APKs) in JDK 7.
Create a debug.keystore
Android needs a debug keystore file to install to devices and distribute non-release APKs. If you have used the SDK before and have built projects, ant or eclipse probably generated one for you (In Linux and OSX, you can find it in the ~/.android folder).
If you can’t find it or need to generate one, the keytool command from the JDK can be used for this purpose:
keytool -keyalg RSA -genkeypair -alias androiddebugkey -keypass android -keystore debug.keystore -storepass android -dname "CN=Android Debug,O=Android,C=US" -validity 9999
Make sure you have adb
Android Debug Bridge (adb) is the command line tool used to communicate with Android devices. It’s installed with the SDK, but you may need to install one (any) of the Android API levels for it to be installed in the SDK directory.
Setting it up in Godot
Enter the Editor Settings screen. This screens contains the editor settings for the user account in the computer (It’s independent from the project).
Scroll down to the section where the Android settings are located:
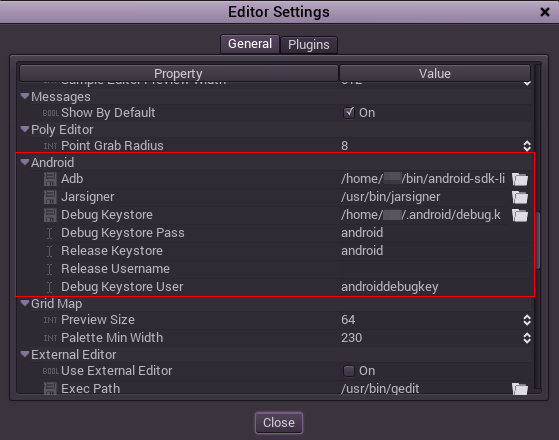
In that screen, the path to 3 files needs to be set:
- The adb executable (adb.exe on Windows)
- The jarsigner executable (from JDK 6 or 8)
- The debug keystore
Once that is configured, everything is ready to export to Android!
© 2014–2020 Juan Linietsky, Ariel Manzur and the Godot community
Licensed under the Creative Commons Attribution Unported License v3.0.
https://docs.godotengine.org/en/2.1/learning/workflow/export/exporting_for_android.html