Active Storage Overview
This guide covers how to attach files to your Active Record models.
After reading this guide, you will know:
- How to attach one or many files to a record.
- How to delete an attached file.
- How to link to an attached file.
- How to use variants to transform images.
- How to generate an image representation of a non-image file, such as a PDF or a video.
- How to send file uploads directly from browsers to a storage service, bypassing your application servers.
- How to clean up files stored during testing.
- How to implement support for additional storage services.
Chapters
- What is Active Storage?
- Setup
- Attaching Files to Records
- Removing Files
- Linking to Files
- Downloading Files
- Transforming Images
- Previewing Files
- Direct Uploads
- Discarding Files Stored During System Tests
- Implementing Support for Other Cloud Services
1 What is Active Storage?
Active Storage facilitates uploading files to a cloud storage service like Amazon S3, Google Cloud Storage, or Microsoft Azure Storage and attaching those files to Active Record objects. It comes with a local disk-based service for development and testing and supports mirroring files to subordinate services for backups and migrations.
Using Active Storage, an application can transform image uploads with ImageMagick, generate image representations of non-image uploads like PDFs and videos, and extract metadata from arbitrary files.
2 Setup
Active Storage uses two tables in your application’s database named active_storage_blobs and active_storage_attachments. After creating a new application (or upgrading your application to Rails 5.2), run rails active_storage:install to generate a migration that creates these tables. Use rails db:migrate to run the migration.
Declare Active Storage services in config/storage.yml. For each service your application uses, provide a name and the requisite configuration. The example below declares three services named local, test, and amazon:
local:
service: Disk
root: <%= Rails.root.join("storage") %>
test:
service: Disk
root: <%= Rails.root.join("tmp/storage") %>
amazon:
service: S3
access_key_id: ""
secret_access_key: "" Tell Active Storage which service to use by setting Rails.application.config.active_storage.service. Because each environment will likely use a different service, it is recommended to do this on a per-environment basis. To use the disk service from the previous example in the development environment, you would add the following to config/environments/development.rb:
# Store files locally. config.active_storage.service = :local
To use the Amazon S3 service in production, you add the following to config/environments/production.rb:
# Store files on Amazon S3. config.active_storage.service = :amazon
Continue reading for more information on the built-in service adapters (e.g. Disk and S3) and the configuration they require.
2.1 Disk Service
Declare a Disk service in config/storage.yml:
local:
service: Disk
root: <%= Rails.root.join("storage") %> 2.2 Amazon S3 Service
Declare an S3 service in config/storage.yml:
amazon: service: S3 access_key_id: "" secret_access_key: "" region: "" bucket: ""
Add the aws-sdk-s3 gem to your Gemfile:
gem "aws-sdk-s3", require: false
The core features of Active Storage require the following permissions: s3:ListBucket, s3:PutObject, s3:GetObject, and s3:DeleteObject. If you have additional upload options configured such as setting ACLs then additional permissions may be required.
If you want to use environment variables, standard SDK configuration files, profiles, IAM instance profiles or task roles, you can omit the access_key_id, secret_access_key, and region keys in the example above. The Amazon S3 Service supports all of the authentication options described in the AWS SDK documentation.
2.3 Microsoft Azure Storage Service
Declare an Azure Storage service in config/storage.yml:
azure: service: AzureStorage storage_account_name: "" storage_access_key: "" container: ""
Add the azure-storage gem to your Gemfile:
gem "azure-storage", require: false
2.4 Google Cloud Storage Service
Declare a Google Cloud Storage service in config/storage.yml:
google:
service: GCS
credentials: <%= Rails.root.join("path/to/keyfile.json") %>
project: ""
bucket: "" Optionally provide a Hash of credentials instead of a keyfile path:
google:
service: GCS
credentials:
type: "service_account"
project_id: ""
private_key_id: <%= Rails.application.credentials.dig(:gcs, :private_key_id) %>
private_key: <%= Rails.application.credentials.dig(:gcs, :private_key).dump %>
client_email: ""
client_id: ""
auth_uri: "https://accounts.google.com/o/oauth2/auth"
token_uri: "https://accounts.google.com/o/oauth2/token"
auth_provider_x509_cert_url: "https://www.googleapis.com/oauth2/v1/certs"
client_x509_cert_url: ""
project: ""
bucket: "" Add the google-cloud-storage gem to your Gemfile:
gem "google-cloud-storage", "~> 1.8", require: false
2.5 Mirror Service
You can keep multiple services in sync by defining a mirror service. When a file is uploaded or deleted, it's done across all the mirrored services. Mirrored services can be used to facilitate a migration between services in production. You can start mirroring to the new service, copy existing files from the old service to the new, then go all-in on the new service. Define each of the services you'd like to use as described above and reference them from a mirrored service.
s3_west_coast:
service: S3
access_key_id: ""
secret_access_key: ""
region: ""
bucket: ""
s3_east_coast:
service: S3
access_key_id: ""
secret_access_key: ""
region: ""
bucket: ""
production:
service: Mirror
primary: s3_east_coast
mirrors:
- s3_west_coast Files are served from the primary service.
This is not compatible with the direct uploads feature.
3 Attaching Files to Records
3.1 has_one_attached
The has_one_attached macro sets up a one-to-one mapping between records and files. Each record can have one file attached to it.
For example, suppose your application has a User model. If you want each user to have an avatar, define the User model like this:
class User < ApplicationRecord has_one_attached :avatar end
You can create a user with an avatar:
class SignupController < ApplicationController
def create
user = User.create!(user_params)
session[:user_id] = user.id
redirect_to root_path
end
private
def user_params
params.require(:user).permit(:email_address, :password, :avatar)
end
end Call avatar.attach to attach an avatar to an existing user:
Current.user.avatar.attach(params[:avatar])
Call avatar.attached? to determine whether a particular user has an avatar:
Current.user.avatar.attached?
3.2 has_many_attached
The has_many_attached macro sets up a one-to-many relationship between records and files. Each record can have many files attached to it.
For example, suppose your application has a Message model. If you want each message to have many images, define the Message model like this:
class Message < ApplicationRecord has_many_attached :images end
You can create a message with images:
class MessagesController < ApplicationController
def create
message = Message.create!(message_params)
redirect_to message
end
private
def message_params
params.require(:message).permit(:title, :content, images: [])
end
end Call images.attach to add new images to an existing message:
@message.images.attach(params[:images])
Call images.attached? to determine whether a particular message has any images:
@message.images.attached?
3.3 Attaching File/IO Objects
Sometimes you need to attach a file that doesn’t arrive via an HTTP request. For example, you may want to attach a file you generated on disk or downloaded from a user-submitted URL. You may also want to attach a fixture file in a model test. To do that, provide a Hash containing at least an open IO object and a filename:
@message.image.attach(io: File.open('/path/to/file'), filename: 'file.pdf') When possible, provide a content type as well. Active Storage attempts to determine a file’s content type from its data. It falls back to the content type you provide if it can’t do that.
@message.image.attach(io: File.open('/path/to/file'), filename: 'file.pdf', content_type: 'application/pdf') If you don’t provide a content type and Active Storage can’t determine the file’s content type automatically, it defaults to application/octet-stream.
4 Removing Files
To remove an attachment from a model, call purge on the attachment. Removal can be done in the background if your application is setup to use Active Job. Purging deletes the blob and the file from the storage service.
# Synchronously destroy the avatar and actual resource files. user.avatar.purge # Destroy the associated models and actual resource files async, via Active Job. user.avatar.purge_later
5 Linking to Files
Generate a permanent URL for the blob that points to the application. Upon access, a redirect to the actual service endpoint is returned. This indirection decouples the public URL from the actual one, and allows, for example, mirroring attachments in different services for high-availability. The redirection has an HTTP expiration of 5 min.
url_for(user.avatar)
To create a download link, use the rails_blob_{path|url} helper. Using this helper allows you to set the disposition.
rails_blob_path(user.avatar, disposition: "attachment")
If you need to create a link from outside of controller/view context (Background jobs, Cronjobs, etc.), you can access the rails_blob_path like this:
Rails.application.routes.url_helpers.rails_blob_path(user.avatar, only_path: true)
6 Downloading Files
If you need to process the blobs on the server side, such as, when performing analysis or further conversions, you can download the blob and get a binary object:
binary = user.avatar.download
In some cases you might want to convert that into an actual file on the disk to pass the file path to external programs (such as virus scanners, converters, optimizers, minifiers, etc.). In this case you can include the ActiveStorage::Downloading module into your class which provides helpers to download directly into files while avoiding to store the file into memory. ActiveStorage::Downloading expects a blob method to be defined.
class VirusScanner
include ActiveStorage::Downloading
attr_reader :blob
def initialize(blob)
@blob = blob
end
def scan
download_blob_to_tempfile do |file|
system 'scan_virus', file.path
end
end
end By default, download_blob_to_tempfile creates files in Dir.tmpdir. If you need to use another directory, override ActiveStorage::Downloading#tempdir in your class:
class VirusScanner
include ActiveStorage::Downloading
# ...
private
def tempdir
'/path/to/tmp'
end
end If the external program is run as a separate program, you might also want to chmod the file and it's directory, as it is inaccessible by other users because Tempfile will set the permissions to 0600.
7 Transforming Images
To create a variation of the image, call variant on the Blob. You can pass any MiniMagick supported transformation to the method.
To enable variants, add mini_magick to your Gemfile:
gem 'mini_magick'
When the browser hits the variant URL, Active Storage will lazily transform the original blob into the specified format and redirect to its new service location.
<%= image_tag user.avatar.variant(resize: "100x100") %>
8 Previewing Files
Some non-image files can be previewed: that is, they can be presented as images. For example, a video file can be previewed by extracting its first frame. Out of the box, Active Storage supports previewing videos and PDF documents.
<ul>
<% @message.files.each do |file| %>
<li>
<%= image_tag file.preview(resize: "100x100>") %>
</li>
<% end %>
</ul> Extracting previews requires third-party applications, ffmpeg for video and mutool for PDFs. These libraries are not provided by Rails. You must install them yourself to use the built-in previewers. Before you install and use third-party software, make sure you understand the licensing implications of doing so.
9 Direct Uploads
Active Storage, with its included JavaScript library, supports uploading directly from the client to the cloud.
9.1 Direct upload installation
-
Include
activestorage.jsin your application's JavaScript bundle.Using the asset pipeline:
//= require activestorage
Using the npm package:
import * as ActiveStorage from "activestorage" ActiveStorage.start()
-
Annotate file inputs with the direct upload URL.
<%= form.file_field :attachments, multiple: true, direct_upload: true %>
That's it! Uploads begin upon form submission.
9.2 Direct upload JavaScript events
| Event name | Event target | Event data (event.detail) | Description |
|---|---|---|---|
direct-uploads:start | <form> | None | A form containing files for direct upload fields was submitted. |
direct-upload:initialize | <input> | {id, file} | Dispatched for every file after form submission. |
direct-upload:start | <input> | {id, file} | A direct upload is starting. |
direct-upload:before-blob-request | <input> | {id, file, xhr} | Before making a request to your application for direct upload metadata. |
direct-upload:before-storage-request | <input> | {id, file, xhr} | Before making a request to store a file. |
direct-upload:progress | <input> | {id, file, progress} | As requests to store files progress. |
direct-upload:error | <input> | {id, file, error} | An error occurred. An alert will display unless this event is canceled. |
direct-upload:end | <input> | {id, file} | A direct upload has ended. |
direct-uploads:end | <form> | None | All direct uploads have ended. |
9.3 Example
You can use these events to show the progress of an upload.
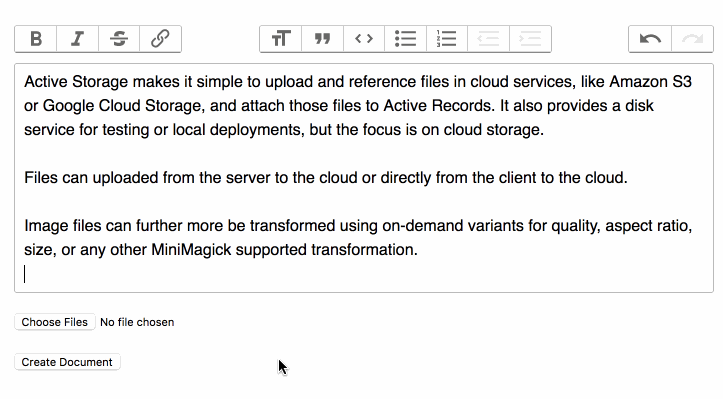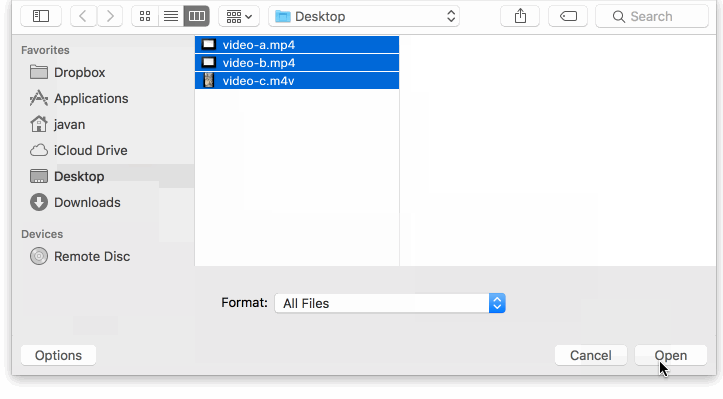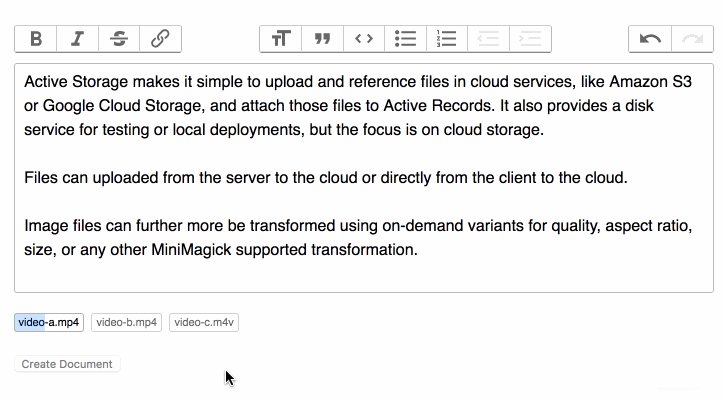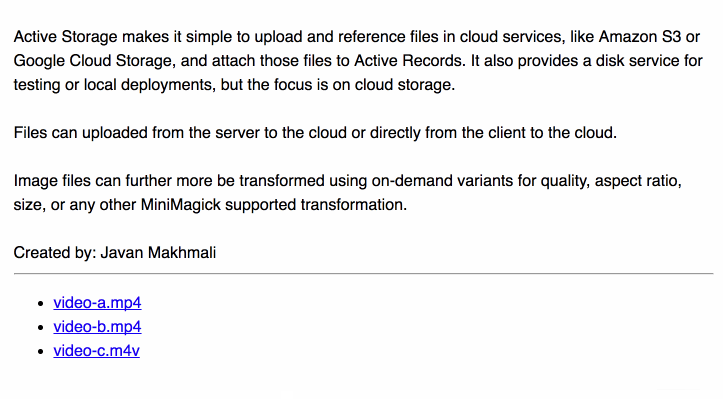
To show the uploaded files in a form:
// direct_uploads.js
addEventListener("direct-upload:initialize", event => {
const { target, detail } = event
const { id, file } = detail
target.insertAdjacentHTML("beforebegin", `
<div id="direct-upload-${id}" class="direct-upload direct-upload--pending">
<div id="direct-upload-progress-${id}" class="direct-upload__progress" style="width: 0%"></div>
<span class="direct-upload__filename">${file.name}</span>
</div>
`)
})
addEventListener("direct-upload:start", event => {
const { id } = event.detail
const element = document.getElementById(`direct-upload-${id}`)
element.classList.remove("direct-upload--pending")
})
addEventListener("direct-upload:progress", event => {
const { id, progress } = event.detail
const progressElement = document.getElementById(`direct-upload-progress-${id}`)
progressElement.style.width = `${progress}%`
})
addEventListener("direct-upload:error", event => {
event.preventDefault()
const { id, error } = event.detail
const element = document.getElementById(`direct-upload-${id}`)
element.classList.add("direct-upload--error")
element.setAttribute("title", error)
})
addEventListener("direct-upload:end", event => {
const { id } = event.detail
const element = document.getElementById(`direct-upload-${id}`)
element.classList.add("direct-upload--complete")
}) Add styles:
/* direct_uploads.css */
.direct-upload {
display: inline-block;
position: relative;
padding: 2px 4px;
margin: 0 3px 3px 0;
border: 1px solid rgba(0, 0, 0, 0.3);
border-radius: 3px;
font-size: 11px;
line-height: 13px;
}
.direct-upload--pending {
opacity: 0.6;
}
.direct-upload__progress {
position: absolute;
top: 0;
left: 0;
bottom: 0;
opacity: 0.2;
background: #0076ff;
transition: width 120ms ease-out, opacity 60ms 60ms ease-in;
transform: translate3d(0, 0, 0);
}
.direct-upload--complete .direct-upload__progress {
opacity: 0.4;
}
.direct-upload--error {
border-color: red;
}
input[type=file][data-direct-upload-url][disabled] {
display: none;
} 9.4 Integrating with Libraries or Frameworks
If you want to use the Direct Upload feature from a JavaScript framework, or you want to integrate custom drag and drop solutions, you can use the DirectUpload class for this purpose. Upon receiving a file from your library of choice, instantiate a DirectUpload and call its create method. Create takes a callback to invoke when the upload completes.
import { DirectUpload } from "activestorage"
const input = document.querySelector('input[type=file]')
// Bind to file drop - use the ondrop on a parent element or use a
// library like Dropzone
const onDrop = (event) => {
event.preventDefault()
const files = event.dataTransfer.files;
Array.from(files).forEach(file => uploadFile(file))
}
// Bind to normal file selection
input.addEventListener('change', (event) => {
Array.from(input.files).forEach(file => uploadFile(file))
// you might clear the selected files from the input
input.value = null
})
const uploadFile = (file) {
// your form needs the file_field direct_upload: true, which
// provides data-direct-upload-url
const url = input.dataset.directUploadUrl
const upload = new DirectUpload(file, url)
upload.create((error, blob) => {
if (error) {
// Handle the error
} else {
// Add an appropriately-named hidden input to the form with a
// value of blob.signed_id so that the blob ids will be
// transmitted in the normal upload flow
const hiddenField = document.createElement('input')
hiddenField.setAttribute("type", "hidden");
hiddenField.setAttribute("value", blob.signed_id);
hiddenField.name = input.name
document.querySelector('form').appendChild(hiddenField)
}
})
} If you need to track the progress of the file upload, you can pass a third parameter to the DirectUpload constructor. During the upload, DirectUpload will call the object's directUploadWillStoreFileWithXHR method. You can then bind your own progress handler on the XHR.
import { DirectUpload } from "activestorage"
class Uploader {
constructor(file, url) {
this.upload = new DirectUpload(this.file, this.url, this)
}
upload(file) {
this.upload.create((error, blob) => {
if (error) {
// Handle the error
} else {
// Add an appropriately-named hidden input to the form
// with a value of blob.signed_id
}
})
}
directUploadWillStoreFileWithXHR(request) {
request.upload.addEventListener("progress",
event => this.directUploadDidProgress(event))
}
directUploadDidProgress(event) {
// Use event.loaded and event.total to update the progress bar
}
} 10 Discarding Files Stored During System Tests
System tests clean up test data by rolling back a transaction. Because destroy is never called on an object, the attached files are never cleaned up. If you want to clear the files, you can do it in an after_teardown callback. Doing it here ensures that all connections created during the test are complete and you won't receive an error from Active Storage saying it can't find a file.
class ApplicationSystemTestCase < ActionDispatch::SystemTestCase
driven_by :selenium, using: :chrome, screen_size: [1400, 1400]
def remove_uploaded_files
FileUtils.rm_rf("#{Rails.root}/storage_test")
end
def after_teardown
super
remove_uploaded_files
end
end If your system tests verify the deletion of a model with attachments and you're using Active Job, set your test environment to use the inline queue adapter so the purge job is executed immediately rather at an unknown time in the future.
You may also want to use a separate service definition for the test environment so your tests don't delete the files you create during development.
# Use inline job processing to make things happen immediately config.active_job.queue_adapter = :inline # Separate file storage in the test environment config.active_storage.service = :local_test
11 Implementing Support for Other Cloud Services
If you need to support a cloud service other than these, you will need to implement the Service. Each service extends ActiveStorage::Service by implementing the methods necessary to upload and download files to the cloud.
Feedback
You're encouraged to help improve the quality of this guide.
Please contribute if you see any typos or factual errors. To get started, you can read our documentation contributions section.
You may also find incomplete content or stuff that is not up to date. Please do add any missing documentation for master. Make sure to check Edge Guides first to verify if the issues are already fixed or not on the master branch. Check the Ruby on Rails Guides Guidelines for style and conventions.
If for whatever reason you spot something to fix but cannot patch it yourself, please open an issue.
And last but not least, any kind of discussion regarding Ruby on Rails documentation is very welcome on the rubyonrails-docs mailing list.
© 2004–2018 David Heinemeier Hansson
Licensed under the Creative Commons Attribution-ShareAlike 4.0 International License.