Aggregators
OpenTSDB was designed to efficiently combine multiple, distinct time series during query execution. But how do you merge individual time series into a single series of data? Aggregation functions provide the means of mathematically merging the different data series into one, giving you a choice of various mathematical operations. Since OpenTSDB doesn't know whether or not a query will return multiple time series, an aggregation function is always required just in case.
Aggregators have two methods of operation:
Aggregation
Since OpenTSDB doesn't know whether a query will return multiple time series until it scans through all of the data, an aggregation function must be specified for every query just in case. When more than one series is found, the two series are aggregated together into a single time series. For each timestamp in the different time series, the aggregator will perform it's computation for each value in every time series at that timestamp. That is, the aggregator will work across all of the time series at each timestamp. The following table illustrates the sum aggregator as it works across time series A and B to produce series Output.
| series | ts0 | ts0+10s | ts0+20s | ts0+30s | ts0+40s | ts0+50s |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| A | 5 | 5 | 10 | 15 | 20 | 5 |
| B | 10 | 5 | 20 | 15 | 10 | 0 |
| Output | 15 | 10 | 30 | 30 | 30 | 5 |
For timestamp ts0 the data points for A and B are summed, i.e. 5 + 10 == 15. Next, the two values for ts1 are summed together to get 10 and so on. Each aggregation function will perform a different mathematical operation.
Interpolation
In the example above, both time series A and B had data points at every time stamp, they lined up neatly. However what happens when two series do not line up? It can be difficult, and sometimes undesired, to synchronize all sources of data to write at the exact same time. For example, if we have 10,000 servers sending 100 system metrics every 5 minutes, that would be a burst of 10M data points in a single second. We would need a pretty beefy network and cluster to accommodate that traffic. Not to mention the system would be sitting idle for the rest of 5 minutes. Instead it makes much more sense to splay the writes over time so that we have an average of 3,333 writes per second to reduce our hardware and network requirements.
How do you sum or find the avg of a number and something that doesn't exist? One option is to simply ignore the data points for all time series at the time stamp where any series is missing data. But if you have two time series and they are simply miss-aligned, your query would return an empty data set even though there is good data in storage, so that's not very useful.
Another option is to define a scalar value (e.g. 0 or the maximum value for a Long) to use whenever a data point is missing. OpenTSDB 2.0 provides a few aggregation methods that substitute a scalar value for missing data points. These are useful when working with distinct value time series such as the number of sales in at a given time.
However sometimes it doesn't make sense to define a scalar for missing data. Often you may be recording a monotonically increasing counter such as the number of bytes transmitted from a network interface. With a counter, we can use interpolation to make a guess as to what the value would be at that point in time. Interpolation takes two points and the time span between them to calculate a best guess value at the time stamp requested.
Take a look at these two time series where the data is simply offset by 10 seconds:
| series | ts0 | ts0+10s | ts0+20s | ts0+30s | ts0+40s | ts0+50s | ts0+60s |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| A | na | 5 | na | 15 | na | 5 | na |
| B | 10 | na | 20 | na | 10 | na | 20 |
When OpenTSDB is calculating an aggregation it starts at the first data point found for any series, in this case it will be the data for B at ts0. We request a value for A at ts0 but there isn't any data there. We know that there is data for A at ts0+10s but since we don't have any value before that, we can't make a guess as to what it would be. Thus we simply return the value for B.
Next we run across a value for A at time ts0+10s. We request a value for ts0+10s from time series B but there isn't one. But B knows there is a value at ts0+20s and we had a value at ts0 so we can now calculate a guess for ts0+10s. The formula for linear interpolation is y = y0 + (y1 - y0) * ((x - x0) / (x1 - x0)) where, for series B, y0 = 10, y1 = 20, x = ts0+10s (or 10), x0 = ts0 (or 0) and x1 = ts0+20s (or 20). Thus we have y = 10 + (20 - 10) * ((10 - 0) / (20 - 0) which will reduce to y = 10 + 10 * (10 / 20) further reducing to y = 10 + 10 * .5 and y = 10 + 5. Therefore B will give us a guestimated value of 15 at ts0+10s.
Iteration continues over every timestamp for which a data point is found for every series returned as a part of the query. The resulting series, using the sum aggregator, will look like this:
| series | ts0 | ts0+10s | ts0+20s | ts0+30s | ts0+40s | ts0+50s | ts0+60s |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| A | na | 5 | na | 15 | na | 5 | na |
| B | 10 | na | 20 | na | 10 | na | 20 |
| Interpolated A | na | 10 | 10 | ||||
| Interpolated B | 15 | 15 | 15 | na | |||
| Summed Result | 10 | 20 | 30 | 25 | 20 | 20 | 20 |
More Examples: For the graphically inclined we have the following examples. An imaginary metric named m is recorded in OpenTSDB. The "sum of m" is the blue line at the top resulting from a query like start=1h-ago&m=sum:m. It's made of the sum of the red line for host=foo and the green line for host=bar:
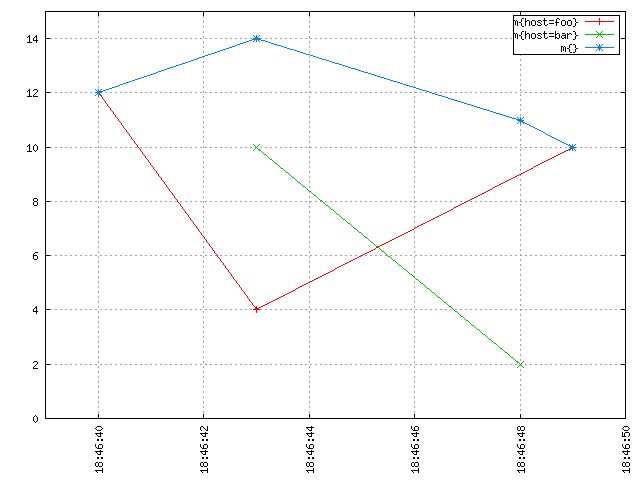
It seems intuitive from the image above that if you "stack up" the red line and the green line, you'd get the blue line. At any discrete point in time, the blue line has a value that is equal to the sum of the value of the red line and the value of the green line at that time. Without interpolation, you get something rather unintuitive that is harder to make sense of, and which is also a lot less meaningful and useful:
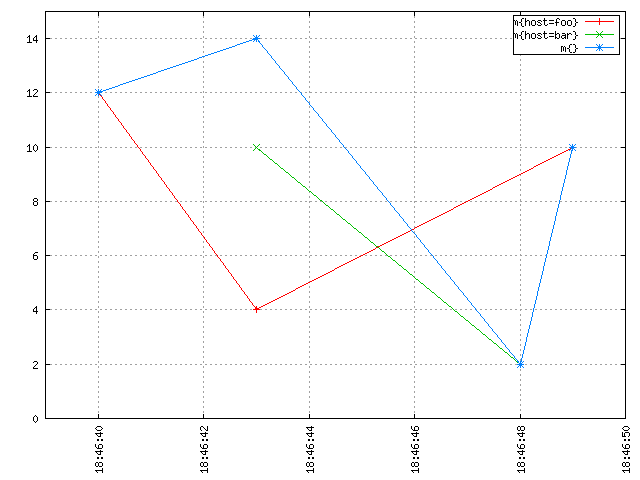
Notice how the blue line drops down to the green data point at 18:46:48. No need to be a mathematician or to have taken advanced maths classes to see that interpolation is needed to properly aggregate multiple time series together and get meaningful results.
At the moment OpenTSDB primarily supports linear interpolation (sometimes shortened "lerp") along with some aggregators that will simply substitute zeros or the max or min value. Patches are welcome for those who would like to add other interpolation methods.
Interpolation is only performed at query time when more than one time series are found to match a query. Many metrics collection systems interpolate on write so that you original value is never recorded. OpenTSDB stores your original value and lets you retrieve it at any time.
Here is another slightly more complicated example that came from the mailing list, depicting how multiple time series are aggregated by average:
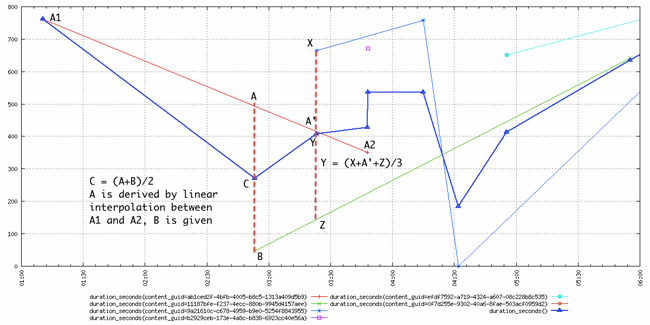
The thick blue line with triangles is the an aggregation with the avg function of multiple time series as per the query start=1h-ago&m=avg:duration_seconds. As we can see, the resulting time series has one data point at each timestamp of all the underlying time series it aggregates, and that data point is computed by taking the average of the values of all the time series at that timestamp. This is also true for the lonely data point of the squared-purple time series, that temporarily boosted the average until the next data point.
Note
Aggregation functions return integer or double values based on the input data points. If both source values are integers in storage, the resulting calculations will be integers. This means any fractional values resulting from the computation will be lopped off, no rounding will occur. If either data point is a floating point value, the result will be a floating point. However if downsampling or rates are enabled, the result will always be a float.
Downsampling
The second method of operation for aggregation functions is downsampling. Since OpenTSDB stores data at the original resolution indefinitely, requesting data for a long time span can return millions of points. This can cause a burden on bandwidth or graphing libraries so it's common to request data at a lower resolution for longer spans. Downsampling breaks the long span of data into smaller spans and merges the data for the smaller span into a single data point. Aggregation functions will perform the same calculation as for an aggregation process but instead of working across data points for multiple time series at a single time stamp, downsampling works across multiple data points within a single time series over a given time span.
For example, take series A and B in the first table under Aggregation. The data points cover a 50 second time span. Let's say we want to downsample that to 30 seconds. This will give us two data points for each series:
| series | ts0 | ts0+10s | ts0+20s | ts0+30s | ts0+40s | ts0+50s |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| A | 5 | 5 | 10 | 15 | 20 | 5 |
| A Downsampled | 35 | 25 | ||||
| B | 10 | 5 | 20 | 15 | 10 | 0 |
| B Downsampled | 50 | 10 | ||||
| Aggregated Result | 85 | 35 |
For early versions of OpenTSDB, the actual time stamps for the new data points will be an average of the time stamps for each data point in the time span. As of 2.1 and later, the timestamp for each point is aligned to the start of a time bucket based on a modulo of the current time and the downsample interval.
Note that when a query specifies a down sampling function and multiple time series are returned, downsampling occurs before aggregation. I.e. now that we have A Downsampled and B Downsampled we can aggregate the two series to come up with the aggregated result on the bottom line.
Fill Policies
With version 2.2 you can specify a fill policy when downsampling to substitute values for use in cross-series aggregations when data points are "missing". Because OpenTSDB does not impose constraints on time alignment or when values are supposed to exist, such constraints must be specified at query time. At serialization time, if all series are missing values for an expected timestamp, nothing is emitted. For example, if a series is writing data every minute from T0 to T4, but for some reason the source fails to write data at T3, only 4 values will be serialized when the user may expect 5. With fill policies you can now choose what value is emitted for T3.
When aggregating multiple series OpenTSDB generally performs linear interpolation when a series is missing a value at a timestamp present in one or more other series. Some aggregators substitute specific values such as zero, min or max values. With fill policies you can modify aggregation behavior by flagging a missing value as a NaN or a scalar such as zero. When a NaN is emitted for a series, it is skipped for all calculations. For example, if a query asks for the average of a metric and one or more series are missing values, substituting a 0 would drive down the average and lerping introduces non-extant values. However with NaNs we can flag the value as missing and skip it in the calculation.
Available polices include:
- None (
none) - The default behavior that does not emit missing values during serialization and performs linear interpolation (or otherwise specified interpolation) when aggregating series. - NaN (
nan) - Emits aNaNin the serialization output when all values are missing in a series. Skips series in aggregations when the value is missing. - Null (
null) - Same behavior as NaN except that during serialization it emits anullinstead of aNaN. - Zero (
zero) - Substitutes a zero when a timestamp is missing. The zero value will be incorporated in aggregated results.
(The terms in parentheses can be used in downsampling specifications, e.g. 1h-sum-nan)
An example with the NaN fill policy and downsampling on 10 seconds:
| series | ts0 | ts0+10s | ts0+20s | ts0+30s | ts0+40s | ts0+50s | ts0+60s |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| A | na | na | na | 15 | na | 5 | na |
| B | 10 | na | 20 | na | na | na | 20 |
| Interpolated A | NaN | NaN | NaN | NaN | NaN | ||
| Interpolated B | NaN | NaN | NaN | NaN | |||
| Summed Result | 10 | NaN | 20 | 15 | NaN | 5 | 20 |
Available Aggregators
The following is a description of the aggregation functions available in OpenTSDB.
| Aggregator | Description | Interpolation |
|---|---|---|
| avg | Averages the data points | Linear Interpolation |
| count | The number of raw data points in the set | Zero if missing |
| dev | Calculates the standard deviation | Linear Interpolation |
| ep50r3 | Calculates the estimated 50th percentile with the R-3 method * | Linear Interpolation |
| ep50r7 | Calculates the estimated 50th percentile with the R-7 method * | Linear Interpolation |
| ep75r3 | Calculates the estimated 75th percentile with the R-3 method * | Linear Interpolation |
| ep75r7 | Calculates the estimated 75th percentile with the R-7 method * | Linear Interpolation |
| ep90r3 | Calculates the estimated 90th percentile with the R-3 method * | Linear Interpolation |
| ep90r7 | Calculates the estimated 90th percentile with the R-7 method * | Linear Interpolation |
| ep95r3 | Calculates the estimated 95th percentile with the R-3 method * | Linear Interpolation |
| ep95r7 | Calculates the estimated 95th percentile with the R-7 method * | Linear Interpolation |
| ep99r3 | Calculates the estimated 99th percentile with the R-3 method * | Linear Interpolation |
| ep99r7 | Calculates the estimated 99th percentile with the R-7 method * | Linear Interpolation |
| ep999r3 | Calculates the estimated 999th percentile with the R-3 method * | Linear Interpolation |
| ep999r7 | Calculates the estimated 999th percentile with the R-7 method * | Linear Interpolation |
| first | Returns the first data point in the set. Only useful for downsampling, not aggregation. (2.3) | Indeterminate |
| last | Returns the last data point in the set. Only useful for downsampling, not aggregation. (2.3) | Indeterminate |
| mimmin | Selects the smallest data point | Maximum if missing |
| mimmax | Selects the largest data point | Minimum if missing |
| min | Selects the smallest data point | Linear Interpolation |
| max | Selects the largest data point | Linear Interpolation |
| none | Skips group by aggregation of all time series. (2.3) | Zero if missing |
| p50 | Calculates the 50th percentile | Linear Interpolation |
| p75 | Calculates the 75th percentile | Linear Interpolation |
| p90 | Calculates the 90th percentile | Linear Interpolation |
| p95 | Calculates the 95th percentile | Linear Interpolation |
| p99 | Calculates the 99th percentile | Linear Interpolation |
| p999 | Calculates the 999th percentile | Linear Interpolation |
| sum | Adds the data points together | Linear Interpolation |
| zimsum | Adds the data points together | Zero if missing |
* For percentile calculations, see the Wikipedia article. For high cardinality calculations, using the estimated percentiles may be more performant.
Avg
Calculates the average of all values across the time span or across multiple time series. This function will perform linear interpolation across time series. It's useful for looking at gauge metrics. Note that even though the calculation will usually result in a float, if the data points are recorded as integers, an integer will be returned losing some precision.
Count
Returns the number of data points stored in the series or range. When used to aggregate multiple series, zeros will be substituted. It's best to use this when downsampling.
Dev
Calculates the standard deviation across a span or time series. This function will perform linear interpolation across time series. It's useful for looking at gauge metrics. Note that even though the calculation will usually result in a float, if the data points are recorded as integers, an integer will be returned losing some precision.
Estimated Percentiles
Calculates various percentiles using a choice of algorithms. These are useful for series with many data points as some data may be kicked out of the calculation. When used to aggregate multiple series, the function will perform linear interpolation. See Wikipedia for details. Implementation is through the Apache Math library.
First & Last
(2.3) These aggregators will return the first or the last data point in the downsampling interval. E.g. if a downsample bucket consists of the series 2, 6, 1, 7 then the first aggregator will return 1 and last will return 7. Note that this aggregator is only useful for downsamplers. When used as a group-by aggregator, the results are indeterminate as the ordering of time series retrieved from storage and held in memory is not consistent from TSD to TSD or execution to execution.
Max
The inverse of min, it returns the largest data point from all of the time series or within a time span. This function will perform linear interpolation across time series. It's useful for looking at the upper bounds of gauge metrics.
MimMin
The "maximum if missing minimum" function returns only the smallest data point from all of the time series or within the time span. This function will not perform interpolation, instead it will return the maximum value for the type of data specified if the value is missing. This will return the Long.MaxValue for integer points or Double.MaxValue for floating point values. See Primitive Data Types for details. It's useful for looking at the lower bounds of gauge metrics.
MimMax
The "minimum if missing maximum" function returns only the largest data point from all of the time series or within the time span. This function will not perform interpolation, instead it will return the minimum value for the type of data specified if the value is missing. This will return the Long.MinValue for integer points or Double.MinValue for floating point values. See Primitive Data Types for details. It's useful for looking at the upper bounds of gauge metrics.
Min
Returns only the smallest data point from all of the time series or within the time span. This function will perform linear interpolation across time series. It's useful for looking at the lower bounds of gauge metrics.
None
(2.3) Skips group by aggregation. This aggregator is useful for fetching the raw data from storage as it will return a result set for every time series matching the filters. Note that the query will throw an exception if used with a downsampler.
Percentiles
Calculates various percentiles. When used to aggregate multiple series, the function will perform linear interpolation. Implementation is through the Apache Math library.
Sum
Calculates the sum of all data points from all of the time series or within the time span if down sampling. This is the default aggregation function for the GUI as it's often the most useful when combining multiple time series such as gauges or counters. It performs linear interpolation when data points fail to line up. If you have a distinct series of values that you want to sum and you do not need interpolation, look at zimsum
ZimSum
Calculates the sum of all data points at the specified timestamp from all of the time series or within the time span. This function does not perform interpolation, instead it substitutes a 0 for missing data points. This can be useful when working with discrete values.
© 2010–2016 The OpenTSDB Authors
Licensed under the GNU LGPLv2.1+ and GPLv3+ licenses.
http://opentsdb.net/docs/build/html/user_guide/query/aggregators.html